Leadership In A Changed World - Your Team
As we emerge from the business disruption, it is not just how we lead our team members to maintain and grow their capabilities, our own leadership ability will also need reinforcement to ensure we underpin the values and mindset critical to achieving the kind of growth and fighting spirit we will now need to see.
In our first article of our Leadership in a Changed World series we explored how You – The Leader are vital to the success of your team and the wider business overall and how you can build resilience in yourself and your team. In this article, we focus on the team itself and how we as leaders can ensure team wellbeing and subsequently team engagement. How we can manage returning to work after furlough and identify best practices to implement while continuing to remain a connected workforce.
This is number two in a series of six articles where we explore leadership in a changed world, in this article we explore:
- Remote Working vs Productivity
- Key Challenges You Will Face
- Psychological Danger vs Psychological Safety
- Fostering Psychology Safety (FPS)
- Psychological Safety and Accountability
- Returning to Work and Building Trust
- Rebuilding Your Team - Stages of Team Development
Remote Working Vs Productivity
In recent months all businesses without exception have been affected by the rapidly changing landscape and the fluctuations in our working practices. With little to no notice we were quickly pulled from our business as usual (BAU) practices and thrust into a changed world. As we transitioned into a new way of working, office-based teams were rapidly moved into exclusively remote working set-ups. Naturally this change brought some disruption to our team performances as well as an initial but short-lived decline in engagement and overall productivity.
It was when we began to organise ourselves remotely and establish new routines, that we started to see a steady rise in our productivity rate begin to take form. Software and apps built for businesses and collaboration have been a massive contributor to our ability to pivot and establish successful remote working environments so quickly. In the first week of January business apps attracted 1.4 million new downloads across iOS and Play Store but in the first week of March downloads jumped to a staggering 6.7 million.[1]
Zoom’s video conferencing software also saw their biggest ever day of app downloads on 8th March with 600,000 downloads compared to 343,000 the week before and just 90,000 downloads two months previously.[2]
In some cases, there may be an engagement and productivity gap between pre-COVID performances and performances today but emerging insights[7] into the impact of COVID-19 on productivity and wellbeing, show that 55% of workers actually believe that their colleagues are just as, if not more, productive now than before lockdown. This doesn’t mean that lockdown came without consequence, in the same survey, 38% of workers say that lockdown has had a negative impact on their wellbeing.
We have reached a critical time and as we move out of lockdown, it is time to start making changes to the way we work, the way we communicate and the way we support each other to begin shaping our near and long-term future.
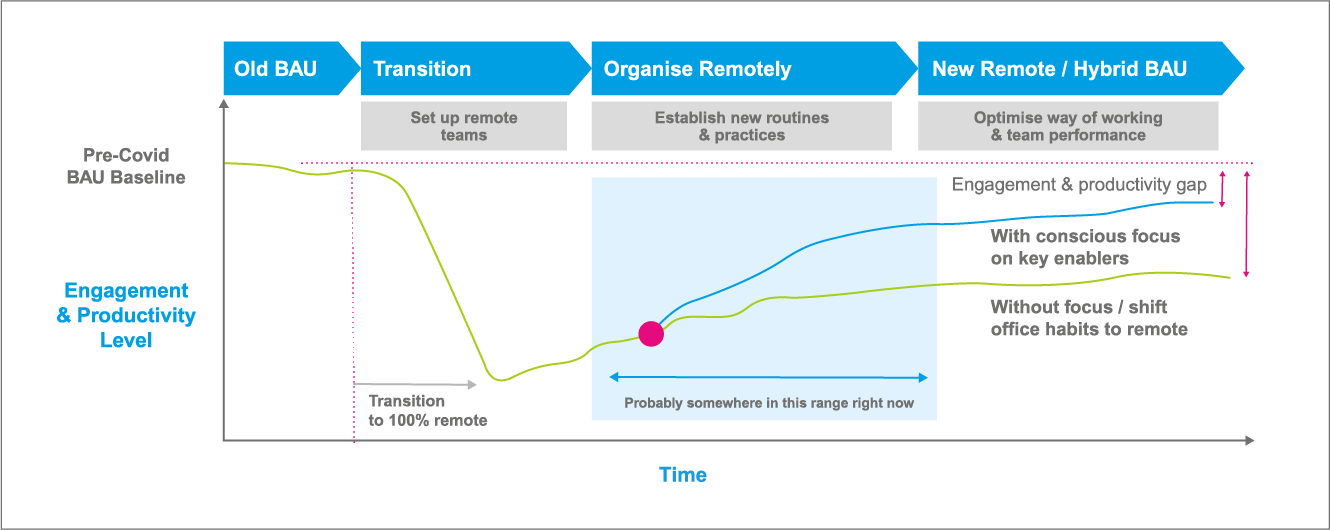
As depicted in this Engagement & Productivity graphic from PwC, we can see that with a conscious focus on our key enablers we can start to make changes that will see workforce productivity rates increase alongside engagement rates through better quality collaboration and communication between team members and teams.
Key Challenges We Will Face
Remote working has created many opportunities, in many ways it has enabled us to address our less effective working practices and establish some better habits, but it has also taken away some things that we all value such as social interactions, a clear definition between time at home and time at work as well as structure and routine.
It is important that we acknowledge the challenges we are facing and set out key practices to actively resolve and overcome them. Left unresolved, these challenges can become blockers to performance and negatively affect engagement.
- Life situation challenges - School closures, health and fitness concerns, domestic disruptions and even isolation anxiety.
- Team working challenges – Prioritising work, conflict resolutions, miscommunications, changing customer demands, and even the orchestration of people.
- Physical and technical constraints - Hardware and software issues, internet bandwidth capability, an overload of collaboration tools and a lack of face- to-face contact.
- Career development opportunities – Downturn in support and peer-to-peer feedback, lack of career development opportunities or vision of possibilities, job security and economic uncertainty
Everyone’s experience can be vastly different and so we need to encourage our teams to be open and honest in the challenges they are facing so we can take active measures to find solutions.
Psychological Danger vs. Psychological Safety
No-one wants to appear incompetent or negative and no-one wants to volunteer that they are struggling with their workload, or that they have made a mistake. To avoid a spotlight of attention or a confrontation we can end up sitting in the ‘Danger’ zone depicted by the graphic and when in this zone, individuals avoid asking questions, contributing to collaborations and suggesting ways to improve working practices.
It is important for our teams to feel safe in an open environment where problems can be shared without fear of retribution. Failure to achieve adequate psychological safety can lead to counterproductive cycles of fear and blame.
The importance of trust in groups and organisations has long been noted by researchers (Kramer 1999). The concepts of psychological safety and trust have much in common; they both describe intrapsychic states involving perceptions of risk or vulnerability, as well as making choices to minimise negative consequences.
Social psychologists have investigated relationships between objective goals and intrapsychic and interpersonal states in a group. Dirks (1999) 4 showed that trust moderates the relationship between goals and performance: when there is a low level of trust in a group, contributions of group members were limited to achieving personal rather than cooperative goals. This can inhibit group-level learning and get in the way of accomplishing a desired organisational change.
On the whole organisations fare much better when challenges are openly discussed and where leaders can respond quickly with solutions.
Our old working practices with shared office spaces, face-to-face meetings and communal spaces offering social opportunities supported open communication for many, while for many introverted members of the team opening up has become easier since working in a remote environment.
The working practices we implement for this new future need to provide opportunities for all team members to feel confident in expressing the challenges they are facing, the solutions they have implemented and their ideas for a successful future.
Fostering Psychological Safety (FPS)
Fostering Psychological Safety (FPS) is a leadership approach that provides a collective vision for learning that encourages people to speak-up, ask questions and share ideas. No-one feels that they will be humiliated or penalised if they speak-up with ideas, questions, concerns, ask for help or admit to a mist
Psychological Safety and Accountability
We need to establish a strong balance between creating a safe environment and ensuring accountability for actions and performance. A safe environment does not mean an environment free from consequence or pressure. Without these things we risk disinterest without the drive to improve and perform at our best. Meanwhile too much accountability can nurture fear and anxiety.
Key actions for tackling negative feelings
Schein and Bennis (1965) 5 discussed the need to create psychological safety for individuals if they are to feel secure and capable of changing. More recently, Schein (1985) 6 argued that psychological safety helps people overcome the defensiveness, or “learning anxiety”, that occurs when people are presented with data that does not support their expectations or hopes.
Team psychological safety is distinct from group cohesiveness, research has shown that cohesiveness can reduce willingness to disagree and challenge others’ views. Psychological safety describes a climate in which the focus can be on transparency through productive discussion that enables early prevention of problems and the accomplishment of shared goals.
Teams that actively practice and nurture transparent working methods can be identified by the following characteristics:
- Open communication and sharing of feelings
- Honest provision of information and progress
- Constructive feedback is sought and welcomed
- Respect between team members and swift conflict resolution
- Admitting wrongdoing and openly seeking assistance for mistakes or problems
To foster a transparent, trust-based culture within your team, start with small changes and build-up a transparency strategy over time. Choose one subject on which everyone has to be regularly updated, and let it be your starting position. Follow-up with your team and check how they feel about this initial change, you can then adjust your strategy accordingly before building on further topics.
Returning to Work and Building Trust
In the coming weeks and month, you will be drawing on all of your leadership skills to help your team navigate through rapid changes and new working practices.
Denial/Resistance
Indicators: Unclear on the need to change, resistant to change, selective listening and responding, cynicism. </p="font-size:>
Leader approach: Adopt a directive approach. Focus on telling, explaining, informing, listening, instructing, asking questions and providing feedback.
Remain calm and supportive, be understanding of the position the individuals are in. Support, instruct, show and demonstrate how things should be done and listen to and observe the actions of your team members. Provide gentle and considered feedback on some specific things, where doing so will be helpful and constructive.
Emotional
Indicators: Moral and productivity decline, fear of the unknown, fear of failure, anger, frustration and confusion, sadness, depression, helplessness, reactive behaviour.
Leader approach: Progress through the steps shown earlier in this article to foster psychological safety.
Understanding and acknowledging the mindset and morale that an individual is experiencing can help you to understand how to lead them to success. Understanding the range of emotions and responses individuals have when experiencing change is crucial as is best depicted by the Kubler-Ross Change Curve.
Acceptance
Indicators: A sense that things may work out OK, less negativity, moral and productivity begin to rise, understanding roles and goals, solutions oriented, sense of achievability.
Leader approach: Support, counsel, show empathy and listen well. Start to empower team members by setting short term goals and providing space to deliver them in their own way.
Commitment
Indicators: Teamwork, roles, goals and linkages are clear. High productivity, positive mindset, excited to come to work. High self-esteem, changes lead to breakthrough results.
Leader approach: Increasingly step away and give people space to perform and own their tasks. Adopt a more coaching approach to leadership. See your role as being to facilitate the success of others. Share ideas, provide feedback, advise and look at ways that you can stretch individuals to improve their performance and development.
To reach a high performance, engaged and productive state we need to help individual team members to let go of limiting mindsets and embrace a forward-thinking approach.
Rebuilding Your Team - Stages of Team Development
Whether you are re-building your team in its new remote working form, or re-forming your team as people return from furlough, you and your team will be working through various stages of team development.
To ensure our teams are happy, engaged and productive it is important that we as leaders understand the stages of team development and how our leadership styles will change at each stage.
Bruce Tuckman first produced the forming–storming– norming–performing model of team development in 1965. He stated that these phases are all necessary and inevitable for the team to grow, face-up to challenges, tackle problems, find solutions, plan work, and deliver results.
Stage 1: Forming - Teams are highly dependent on the leader for guidance and direction. There is little agreement on goals other than those received from the leader. Individual roles and responsibilities are unclear. The leader must be prepared to answer lots of questions about the team’s purpose, objectives and external relationships. Processes are often ignored. Members test the tolerance of the system and the leader.
As a leader, you will direct the team.
Stage 2: Storming - Decisions don’t come easily within the group. Team members vie for position as they attempt to establish themselves in relation to other team members and the leader. Clarity of purpose increases but uncertainties remain. Cliques and factions form and there may be power struggles. The team needs to be focused on its goals to avoid becoming distracted by relationships and emotional issues. Compromises may be required to enable progress.
As a leader, you will coach the team.
Stage 3: Norming - Agreement and consensus forms among the team and they respond well to facilitation by the leader. Roles and responsibilities are clear and accepted. Big decisions are made by group agreement and smaller decisions may be delegated to individuals or small teams within the group.
Commitment and unity is strong, the team may even engage in fun and social activities. The team discusses and develops its processes and working style. There is general respect for the leader and some of the leadership is divided amongst the team.
As a leader, you will facilitate and enable the team.
Stage 4: Performing - The team is more strategically aware and knows clearly why it is doing what it is doing. With a shared vision the team is able to stand on its own feet with no interference or participation from the leader. There is a focus on over-achieving goals, and the team has a high degree of autonomy.
Disagreements occur but now they are resolved within the team positively, and necessary changes to processes and structure are made by the team. The team requires delegated tasks and projects from the leader but do not need to be instructed or assisted. Team members might ask for assistance from the leader with personal and interpersonal development.
As a leader, you will delegate and oversee the team.
No matter how small you may perceive a change to be or how insignificant, you will progress back through the team development stages each time a change happens, and we expect changes to continue for the foreseeable future.
References
- Sensor Tower [Internet] https://sensortower.com/blog /app-revenue-and-downloads-1h-2020
- Forbes [Internet] https://www.forbes.com/sites/ alexkonrad/2020/03/13/zoom-video-coronavirus- eric-yuan-schools/#16c47dc54e71
- Amy C. Edmondson. Associate Professor, Harvard Business School. Managing the risk of learning: Psychological safety in work teams. [Internet] March 15, 2002 https://citeseerx.ist.psu. edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.118.1943&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- Dirks, K. T. (1999). The effects of interpersonal trust on work group performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 84(3), 445–455. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1999-05190-012
- Amy C. Edmondson. Annual Review of Organisational Psychology and Organizational Behaviour 1(1):23-43. 5 March 2014 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275070993 _Psychological_Safety_The_History_Renaissance _and_Future_of_an_Interpersonal_Construct
- Schein, E. (1985). Organizational culture and leadership (1st ed.). https://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=Mnres2PlFLMC &oi=fnd&pg=PR9&dq=Schein,+E.+(1985).+Organizational+cultur e+and+leadership+(1st+ed.).+San+Francisco:+Jossey-Bass+ Publishers.&ots=ookwOb4rSg&sig=CLWMklJkhv6Y6vIL2aUTB yc5xWY#v=onepage&q&f=false
- Deloitte [Internet] Research carried out by Ipson MORI on behalf of Deloitte LLP. https://www2.deloitte.com/uk/en/pages/ consulting/articles/working-during-lockdown-impact-of-covid-19on-productivity-and-wellbeing.htm

















